Our Projects
Cultural Transformation
CulturalKeys’ process of cultural transformation helps organizations implement the changes they want to make. It is an integral part of our research and consulting engagements.
FOSTERING A CULTURE OF COLLABORATION


Problem
- Improve relationships and cooperation in General Motors’ manufacturing plants
- Reduce conflict between hourly and salaried employees, as well as between GM and the United Auto Workers' management
Action
- Collected and compiled employee perspectives of the current and "ideal" plant culture
- Identified collaboration as the key weakness in GM’s ongoing cultural change efforts
- Created a step-by-step model and process for cultural transformation to strengthen collaboration
Solution
- Worked with plant leaders to develop, validate, and implement 10 practical tools including a computer game and a set of assessment metrics to improve collaboration on the plant floor
- Wrote an award-winning book documenting a successful change-management strategy
EXPLAINING MANAGEMENT AND EMPLOYEE CHALLENGES POST ACQUISITION
Problem
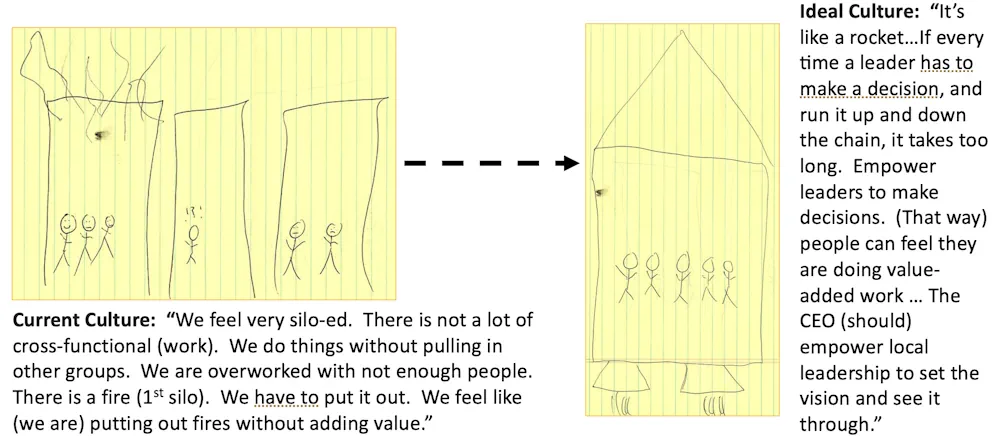
- Until recently, the parent firm made little effort to integrate three companies it acquired one decade earlier
- The parent firm sought to understand its collective culture
Action
- Combined interviews with interviewee drawings across eight sites in four countries to identify prominent cultural themes
- Found that this multicultural corporation suffered from poor performance, which was attributed to inexperienced leadership, “top-down” mandates, decision-making paralysis, a siloed structure, unwieldly systems and processes, and inadequate feedback loops
Solution
- Presented our findings and educated corporate leaders about best practices in today’s corporate organizations
- Recommended problem-solving leadership discussions and workshops to help improve the organizational culture
ENHANCING USER-ORIENTED DESIGN


Problem
- Determine the most appropriate workspace for industrial researchers
- Discover whether this workspace is suitable both cross-culturally and for younger research professionals
Action
- Used mixed methods (i.e., qualitative and quantitative) to build a model of researcher workspace that maximized productivity
- Learned that private offices improved concentration for "heads-down" work and enabled small-group and virtual collaborations without disturbing others
Solution
- Recommended an exception for industrial researchers to the corporate trend for cubicles
- Advised that researchers be assigned private offices to improve their productivity and partnering effectiveness; single offices were subsequently built in domestic and international locations
INNOVATING THROUGH EFFECTIVE GLOBAL PARTNERSHIPS

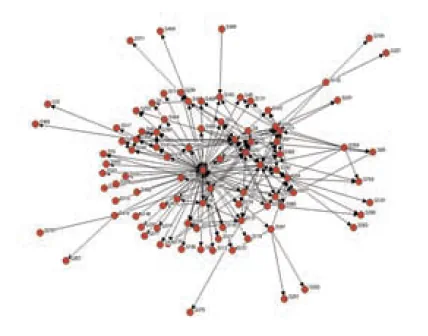
Problem
- Find out the best ways to advance scientific breakthroughs
- Discover how scientists and engineers from an industrial research lab and world-class universities build effective partnerships together
Action
- Used interviews, documents, social-network surveys, observations, and systems-dynamics modeling techniques to understand the partnership life cycle
- Created, tested, and patented a model of relationship effectiveness
Solution
- Developed and disseminated a set of current best practices for developing and maintaining strong and productive relationships between the partners
- Published an edited volume documenting key results and lessons
Consumer Satisfaction
We advocate building connections with consumers so that firms understand and serve them well. Consumers do not want to hear excuses for a service that does not meet expectations or a product that underperforms.
COMMUNICATING CONSUMER VIEWS TO AN INTIMATE APPAREL FIRM


Problem
- Reinvigorate product sales and marketing for a world leader in intimate apparel
- Identify how the firm’s culture affects its retail sales
Action
- Conducted in-home discussions with consumers which revealed their frustration in purchasing matching sets of bras and panties
- Confirmed that stores have few matching sets to sell based on both observation and discussions with salesclerks
- Learned from interviews with corporate employees that "bras don’t talk to panties," an image underscoring the firm’s siloed structure:
- At the home office: Employees responsible for bras work in one area and those responsible for panties in another
- On the sales floor: Bras and panties are sold in different sections of an intimate department
- In manufacturing facilities: Bras are produced in one plant and panties in another
Solution
- Recommended offering more matching sets in the product line
- Proposed dedicated teams have primary responsibility to produce matching sets
- Suggested improved responsiveness for "hot-selling" products (e.g., having a designated production facility)
- Advocated reduction in overall lead time through fewer product offerings and more carryover designs
GUIDING A HOSPITAL TO BECOME “MORE PATIENT-CENTRIC”
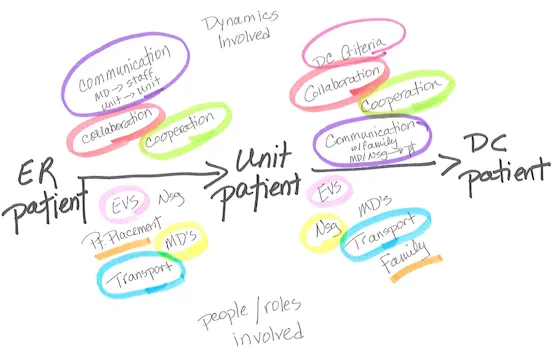

Problem
- Improve the patient experience without any negative effects on the quality of clinical outcomes
- Streamline the flow of patients through the hospital system, reducing patient wait time
- Strategize ways of addressing the hospital’s "siloed" organizational structure
Action
- Analyzed focus group data and found that developing rapport with patients is not fundamental to patient care
- Observed and participated in hospital-wide committees to document the issues they face in improving patient satisfaction scores
- Interviewed and observed hospital employees to learn what accounts for new initiative success
Solution
- Created 16 tools to prioritize the patient experience and create a highly effective and engaged culture
- Form "bottleneck-buster" teams that cross "silos" and support innovation, solve patient flow issues, and empower employees
- Change workplace incentives such as expectations, metrics, and rewards to advance cultural transformation and reduce the likelihood that new initiatives become just another "flavor of the month"
MARKETING THE DISTINCTIVE CULTURE OF A SENIOR COMMUNITY


Problem
- Improve the marketing efforts of an assisted living and nursing care community
- Discover the best ways to describe the culture of this community to prospective residents and their families
Action
- Gathered views of the current and ideal future culture from residents, family members, staff, and volunteers
- Compared views of the current and ideal future culture to identify the community’s perceived strengths and weaknesses
Solution
- Created a "culture story" of this community: its past, current, and ideal future culture
- Offered workshops resulting in the articulation of the care philosophy, now a core part of marketing efforts